10 Incredible Vertical Farming Water Saving Startups
On This Page
Hey there, tech enthusiasts and future-forward thinkers! Olivia Carter here, and today we’re diving headfirst into a topic that’s as critical as it is captivating: how we feed a growing planet while battling an ever-present resource crisis. Specifically, we’re zeroing in on vertical farming water saving—a groundbreaking approach that’s redefining agriculture. Traditional farming guzzles water, accounting for about 70% of freshwater withdrawals globally. But what if there was a way to produce fresh, healthy food with a fraction of that water footprint? Enter vertical farming startups, these ingenious pioneers are not just growing crops upwards; they’re radically rethinking water use in urban agriculture. In fact, their innovations are delivering some amazing water savings, transforming cities into greener, more sustainable hubs. Ready to explore the cutting-edge? Let’s uncover 10 incredible ways urban agriculture is saving our most precious resource.
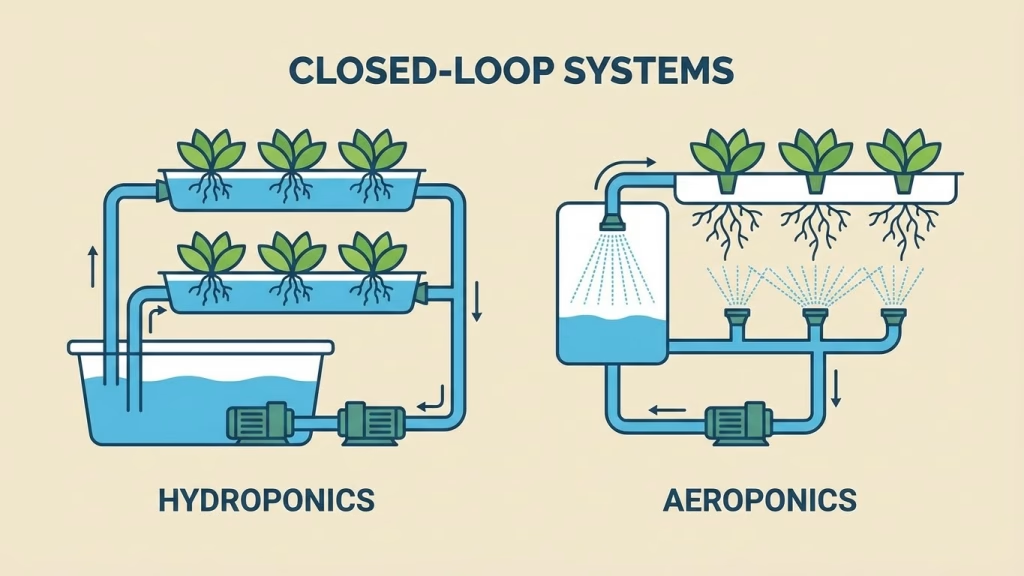
The Power of Closed-Loop Systems Hydroponics and Aeroponics
The most obvious, and arguably most impactful, way vertical farming dramatically cuts water use is through its reliance on soilless cultivation methods. Imagine growing plants not in dirt, but in nutrient-rich water or even just mist. That’s the magic of hydroponics and aeroponics.
Hydroponics: Recycling Every Drop
In hydroponic systems, plants grow with their roots immersed in mineral nutrient solutions. The brilliant part? This water isn’t just used once and then discarded. It’s continuously recirculated, filtered, and monitored for nutrient levels, then fed back to the plants. This closed-loop approach means minimal waste from evaporation or runoff, drastically reducing the amount of water needed compared to field farming. We’re talking about a jaw-dropping 90-95% less water for the same crop yield. It’s like having a hyper-efficient circulatory system for your crops.
Aeroponics: Mist, Not Drench
Taking water efficiency a step further, aeroponics involves suspending plants in the air and misting their roots with a nutrient solution. This method uses even less water than hydroponics because the roots are only exposed to mist for short, controlled periods. The fine mist ensures optimal oxygenation for the roots, leading to faster growth and even greater water savings. Startups leveraging aeroponics are often at the forefront of vertical farming water saving innovations, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
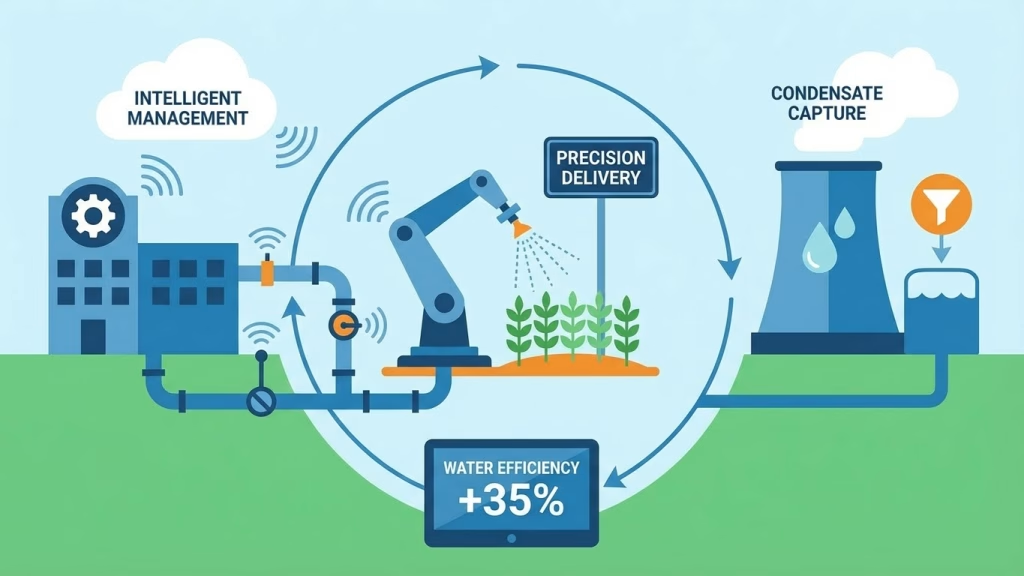
Intelligent Water Management Precision Delivery and Condensate Capture
It’s not just about the growing method; it’s about smart design and leveraging the controlled environment itself to maximize water efficiency.
Precision Nutrient Delivery
Forget wasteful flood irrigation. Vertical farms employ highly precise delivery systems, often akin to drip irrigation, but even more advanced. Water and nutrients are delivered directly to the plant’s root zone, exactly when and where they’re needed. This eliminates water loss due to evaporation from exposed soil surfaces and prevents runoff, ensuring every drop contributes directly to plant growth. Sensors constantly monitor moisture levels around the roots, triggering irrigation only when necessary.
Condensate Capture and Reuse
Indoor vertical farms are essentially giant climate-controlled boxes. Plants transpire, releasing water vapor into the air. Traditional greenhouses often vent this moist air away, but advanced vertical farms capture it. HVAC systems dehumidify the air, collecting the condensed water. This clean, distilled water is then filtered, supplemented with nutrients, and fed back into the irrigation system. It’s a brilliant example of circular economy principles applied to water, ensuring virtually no water leaves the system as waste, further enhancing vertical farming water saving efforts.
Controlled Environments Minimizing Evaporation and Runoff
The very nature of Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA), which underpins vertical farming, is inherently water-efficient.
Eliminating Environmental Variables
When plants are grown indoors, they aren’t exposed to the elements like wind or direct, scorching sun. These factors accelerate evaporation in open fields. Inside a vertical farm, temperature, humidity, and airflow are meticulously controlled. This stable environment drastically reduces water loss from plant surfaces and growing mediums, meaning less water is needed to keep plants hydrated and thriving. It’s a far cry from a sun-baked field losing water to the atmosphere.
No Soil Runoff or Leaching
Traditional agriculture often battles with water runoff carrying pesticides, herbicides, and excess fertilizers into rivers and groundwater, a process known as leaching. Vertical farms, being soilless, eliminate this problem entirely. The closed systems prevent any nutrient-laden water from escaping into the environment, protecting natural water sources from pollution and ensuring all applied water and nutrients are utilized by the crops. This ecological benefit is as significant as the direct water savings and a key aspect of vertical farming water saving principles.
Localizing Food Systems Reducing Transport and Waste
The water-saving benefits of vertical farming extend beyond the growing facility itself, influencing the entire food supply chain.
Reduced “Food Miles” and Associated Water Use
When food travels across continents, a hidden water cost accrues—the water used in processing, packaging, and even the fuel production for transport. By locating farms within or very close to urban consumption centers, vertical farming significantly reduces “food miles.” This shortens the supply chain, minimizes the need for extensive processing to extend shelf life, and cuts down on the embedded water use that would otherwise be spent during these post-harvest stages. It’s a holistic approach to vertical farming water saving.
Minimizing Food Waste and Its Virtual Water Footprint
Globally, a significant portion of food produced is wasted before it reaches the consumer. Every item of wasted food also means wasted “virtual water”—the water used to grow, process, and transport it. Vertical farms, by growing on demand and being geographically closer to consumers, can dramatically reduce post-harvest losses and retail waste. Fresh produce gets to shelves faster, stays fresh longer, and is less likely to spoil, thereby saving all the water that went into producing that wasted food. It’s a silent but powerful contributor to global water conservation.
Harnessing Innovation Data-Driven Optimization and Advanced Capture
The future of vertical farming is deeply intertwined with technological advancements, continuously refining its water efficiency.
AI and IoT for Optimal Water Use
Modern vertical farms are data powerhouses. Equipped with an array of IoT sensors, they constantly monitor everything from temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels to plant growth, nutrient uptake, and water absorption rates. Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms then process this data, making real-time adjustments to irrigation schedules and nutrient delivery, ensuring plants receive the exact amount of water they need, no more, no less. This hyper-optimization eliminates guesswork and further minimizes waste, driving down the overall water footprint. Research consistently shows that such data-driven precision farming achieves unparalleled water efficiency.
Recycling Water from Plant Transpiration
Building on the condensate capture concept, some advanced vertical farming systems are exploring even more sophisticated ways to capture and reuse water released by plants. Transpiration is a natural process where plants release water vapor through their leaves. Instead of just general dehumidification, new technologies are being developed to more efficiently collect and purify this specific transpired water, turning what would typically be a loss into a reusable resource within the closed-loop system. It’s a testament to the ingenuity pushing vertical farming water saving to new heights.
How Will Vertical Farming Redefine Our Water Future?
The innovations being spearheaded by vertical farming startups aren’t just incremental improvements; they represent a paradigm shift in how we approach agriculture and water management. By bringing food production closer to urban centers and employing cutting-edge technologies, these enterprises are demonstrating that it’s entirely possible to feed a growing population with significantly less water, land, and energy. From closed-loop hydroponics to AI-driven precision irrigation and sophisticated condensate capture, every facet of vertical farming is engineered for efficiency. As water scarcity becomes an increasingly pressing global challenge, these urban agriculture pioneers are not just growing crops; they’re cultivating a more sustainable, water-secure future for us all. The seeds of change have been planted, and they’re flourishing in ways we’ve only just begun to imagine.




