5 Mind-Blowing Bio-Hybrid Robots Building an Amazing Future
On This Page
Ever imagined a machine that could heal itself, or a tiny robot powered by actual living muscle cells? Welcome to the thrilling, sometimes unsettling, frontier of bio-hybrid robotics. This isn’t just science fiction anymore; it’s the audacious reality where biology meets engineering, creating machines that leverage the incredible power and adaptability of living tissues.
Bio-hybrid robots are ushering in an era where the lines between organic and synthetic blur, promising revolutionary breakthroughs across medicine, environmental science, and even space exploration. These aren’t your typical metal-and-wire contraptions. We’re talking about devices that integrate living cells, tissues, or even entire organisms as their functional components – for movement, sensing, or self-repair. It’s a game-changer, and today, we’re diving into five mind-blowing ways these bio-hybrid robots are already transforming our world.
The Pulse of Precision Medicine Bio-Hybrid Robots for Delivery
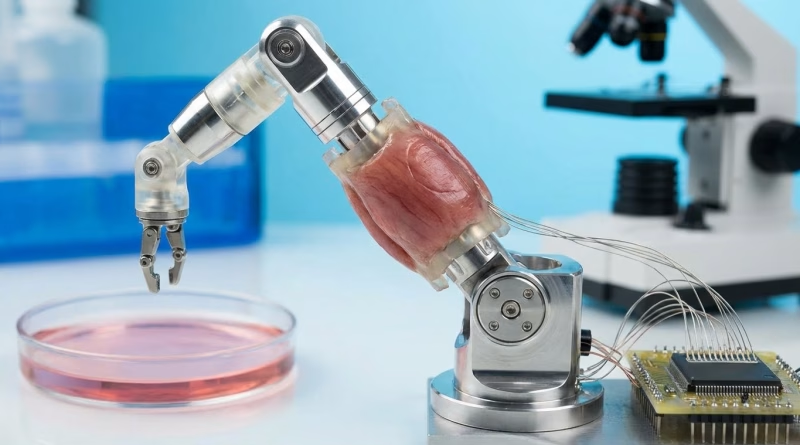
Imagine a robot so small it can navigate your bloodstream, delivering medication directly to a tumor cell without affecting healthy tissue. This isn’t a pipe dream; it’s one of the most exciting applications of bio-hybrid robots. Researchers are developing microscopic robots, often just a few hundred micrometers long, that use living muscle cells – typically from rats or human stem cells – as biological actuators. These cells, when stimulated (either electrically or chemically), contract, providing the propulsion needed for the tiny robot to move. Think of it like a biological propeller or an oar.
The precision offered by these bio-hybrid robots is unparalleled. They can be guided through complex biological environments, reaching targets that conventional methods struggle with. Beyond drug delivery, these muscle-powered micro-bots could perform minimally invasive surgeries, clear arterial blockages, or even facilitate tissue regeneration. The idea of living tissue powering a machine inside your body might sound futuristic, but the potential for targeted, less invasive treatments is truly revolutionary, pushing the boundaries of what precision medicine can achieve.
Soft Robotics Gets a Biological Boost with Bio-Hybrid Actuators
Traditional robots are rigid, clunky, and often ill-suited for interacting with delicate environments or performing tasks that require flexibility. Enter soft robotics, a field focused on creating robots from compliant materials. Now, imagine integrating living muscle tissue into these soft robots, allowing them to bend, grip, and move with unprecedented fluidity and naturalness. This is precisely what bio-hybrid robots are doing for soft robotics.
Scientists have engineered soft robots that incorporate bundles of skeletal muscle tissue or even cardiac muscle cells. These biological components act as sophisticated actuators, contracting and expanding to produce movement similar to how our own muscles work. This approach offers several advantages: natural responsiveness, energy efficiency (as the cells perform work directly), and the potential for self-repair if the tissue is damaged. Imagine soft grippers that can delicately handle fragile objects, or search-and-rescue robots that can squeeze through tight spaces, powered by living biological engines. The integration of living tissue allows these bio-hybrid robots to mimic biological systems in ways purely mechanical designs simply cannot.
Engineering Immortality Self-Healing Bio-Hybrid Systems
One of the biggest challenges with traditional machines is wear and tear; once a component breaks, it needs repair or replacement. Living organisms, however, possess an incredible ability to self-heal. What if robots could do the same? Bio-hybrid robots are making this a reality by incorporating living components that can detect and repair damage.
Researchers are exploring ways to embed biological materials – like self-assembling proteins or even living cells – into robotic structures. If a microscopic crack forms, these biological elements can be stimulated to grow and fill the void, restoring the robot’s integrity. This goes beyond mere material science; it’s about creating machines with a biological repair crew built right in. While still in early stages, the implications are vast. Robots in harsh environments, from deep space to contaminated zones, could maintain operational readiness for longer, reducing the need for human intervention and costly repairs. This revolutionary aspect of bio-hybrid robots could drastically extend the lifespan and resilience of future autonomous systems.
Powering the Future Bio-Hybrid Energy Harvesting
Energy is the lifeblood of any machine, and for bio-hybrid robots, researchers are exploring innovative ways to harness power from biological processes themselves. Instead of relying solely on batteries or external power sources, some bio-hybrid systems are designed to convert metabolic energy from living cells or organisms into electrical power to run their synthetic components. Think of it as a tiny, organic power plant.
For example, microbial fuel cells use bacteria to break down organic matter and generate electricity. When integrated into a robot, these could provide a continuous, sustainable power source, especially in environments rich in organic nutrients. Another fascinating avenue involves using the natural electrochemical gradients within living tissues to generate small amounts of power. While not yet capable of powering large, complex machines, these methods could provide auxiliary power for sensors, communication modules, or even provide energy for the biological actuators themselves, creating truly self-sustaining bio-hybrid robots. This sustainable approach to energy is crucial for long-duration missions where recharging is impractical.
Sentient Machines Environmental Sensing Bio-Hybrid Robots
Living organisms have evolved incredibly sensitive ways to detect changes in their environment – from subtle chemical shifts to temperature fluctuations. Bio-hybrid robots are leveraging this natural sensing capability by integrating living cells or tissues directly into their sensory systems. Imagine a robot that can “smell” pollutants with the accuracy of a dog’s nose, or detect subtle changes in water quality using live bacterial cultures.
For instance, genetically engineered bacteria can be used as biosensors within bio-hybrid robots. These bacteria might glow or change color in the presence of specific toxins, providing an immediate, highly sensitive response. Similarly, neural networks cultivated from living brain cells could theoretically be interfaced with robotic systems to provide unparalleled pattern recognition and adaptive learning capabilities. This level of biological integration allows bio-hybrid robots to perceive and interact with their surroundings in ways that traditional, purely electronic sensors simply cannot match, opening doors for advanced environmental monitoring, biomedical diagnostics, and even novel forms of human-machine interfaces. You can learn more about groundbreaking research in this field from institutions like Harvard’s Wyss Institute, which is at the forefront of bio-inspired engineering.
Are We Ready for a World of Living Machines?
The journey into bio-hybrid robotics is just beginning, but the implications are staggering. From precision medical interventions to self-sustaining environmental guardians, these machines promise to revolutionize nearly every aspect of our technological landscape. However, as we venture deeper into this convergence of biology and engineering, ethical considerations and safety protocols become paramount. How do we ensure these living machines are developed responsibly? What are the long-term societal impacts? One thing is clear: bio-hybrid robots are not just a fascinating scientific curiosity; they are a powerful glimpse into a future where the definition of “machine” is profoundly reshaped, offering amazing possibilities we’re only just beginning to comprehend. Get ready, because the future is alive.